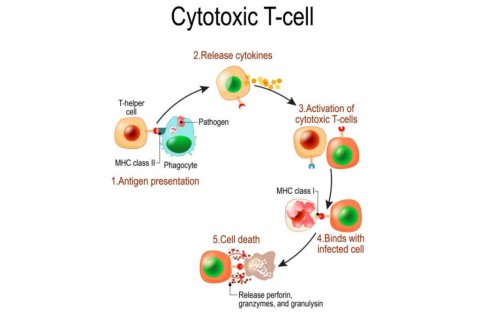
We all know someone that has had cancer. In our family my dad and sister are cancer survivors. And although this disease is very close to all of us we often don't know what to do when it comes to exercise and cancer. Should you exercise or not? Does it help or harm? I'm not an oncologist and so don't take these ramblings as medical advice. But I still keep an eye on the research and stay informed as more information on this topic becomes available. A paper out of the Karolinska Institute in Sweden gives some promise for exercise with cancer. The authors looked at over 100 studies, involving over one million adults and 13 different types of cancer. What they found was that exercisers had better outcomes, related to their cancer, than those who didn't exercise. It appeared that exercise helped prevent the onset of cancer. And it helped the body fight back more effectively against the cancer. So how does this happen? Well it appears there are particular immune cells, cytotoxic T cells, that are positively influenced by the effects of exercise. These immune cells, aka killer T cells, have enhanced function with individuals that exercise. Representation of the role of T cells Source: https://www.thoughtco.com/t-cells-meaning-373354 Researchers have transferred the T cells of mice that exercise, to non-exercising mice, and seen tumour reductions. More specifically it appears that certain metabolites are produced during exercise that play a role. Lactate, in particular, seems to bolster T cell activity. When mice where given sodium L-lactate there was an increase in T cell activity and greater decrease in tumour growth. While this all sounds promising there are a few things to keep in mind: The papers reviewed and cited included adults with cancer. We might expect similar results with children but the...
How to Improve Lactate Threshold
- Chris Collins
- Fitness
- Training
- 1847 Hits
- 0 Comments
-
In the last post we talked about why people may use a heart rate monitor. Click here if you missed that post. Besides the most common value people check when they use a heart rate monitor, which is calories burned there are a number of other benefits to using one. But first we should do a quick review so we're all on the same page as to what we're talking about. So here's a quick recap of some of the terms you may get thrown around on blogs and in training circles. Anaerobic Threshold - This is the intensity of exercise where energy demands cannot solely be supplied by oxygen and must be supplemented by anaerobic metabolism. Lactate Threshold - As the demands for energy produced anaerobically increase there is a lactate accumulation in the blood as well. Lactate accumulates because it is being produced faster than it can be cleared from the blood. The units for this measure may be expressed as mmol/L. VO2max - This is the highest rate of oxygen consumption at maximal intensity exercise. In other words when we are below our VO2max we can still consume more oxygen with increasing intensity. However once our VO2max has been achieved further increases with intensity will not result in increased oxygen consumption. In terms of units it is usually expressed as ml/kg/min. If I've worked with you before or you are familiar with our coaching style at Okanagan Peak Performance Inc you'll know we use a lot of analogies. So here's the analogy for lactate threshold and VO2max. Lactate Threshold is like the floor in your home. VO2max is like the ceiling. With my own training I would like to improve my lactate threshold. In other words I want to raise the floor up towards the ceiling. Let's throw...